Periodontal Disease (Gum Disease)
What is periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease, also referred to as gum disease, is an infection affecting the supporting structures of the teeth, including the gums and bone. It is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth and gums, which leads to inflammation and infection. If left untreated, periodontal disease can progress to more severe stages, potentially resulting in tooth loss.
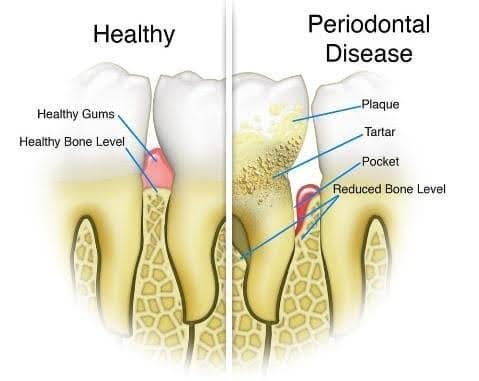
Plaque naturally accumulates on the teeth throughout the day. Regular brushing twice daily helps prevent plaque from hardening into calculus (tartar). This occurs when minerals in the saliva cause the plaque to solidify, with tartar commonly forming on the inside surfaces of the lower teeth. In response, the body’s immune system sends white blood cells to the gums to initiate the healing process, which results in inflammation. If plaque and tartar are not effectively removed, the gums and supporting bone may begin to recede over time. This progression is gradual and often goes unnoticed without regular dental examinations.
The positive aspect is that plaque can be effectively removed with daily brushing. However, once plaque has hardened into tartar, professional removal by a dentist or periodontist using specialised instruments is necessary.
Causes of Periodontal Disease
- Poor Oral Hygiene
- Smoking or Chewing Tobacco
- Genetics
- Hormonal Changes (i.e during Puberty, pregnancy, menopause etc)
- Medications
- Poor Nutrition
- Health Conditions, systemic diseases and stress
Gum disease affects your overall health and has been associated with the following systemic conditions: heart disease and some strokes, diabetes, preterm low-birth weight babies, Rheumatoid arthritis, respiratory diseases and more.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease include the following: Swollen or bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, generalised pain while chewing, loose teeth, and gums that recede from teeth, making teeth appear longer
The stages of Periodontal disease:
Periodontal disease presents itself in 3 different stages:
- Gingivitis – this is the mild inflammation of the gums and usually associated with gum swelling and bleeding on brushing/ flossing. Bleeding gums are a sign of disease, as healthy gums do not bleed. Gingivitis is reversible with professional treatment and good regular oral care at home.
- Chronic Periodontitis – this is one of the most common forms of infections in humans, affecting about 20% of the adult population. This condition is not usually painful and can therefore go undetected for a long time. If gingivitis is not controlled and reversed, it eventually turns into Periodontitis. This ultimately leads to the loss of the supporting structures around the teeth (gum and bone). While this condition cannot be reversed, it can be stabilised and stopped from progressing further.
- Advanced/ Aggressive Periodontitis – a severe form of gum disease which can result in the loss of many/all of the teeth if left untreated. It can also lead to tooth abscesses and severe pain associated with this. This is a difficult condition to manage and stabilise and usually requires regular treatment with a specialist (periodontist) and commitment from the patient to maintain good oral hygiene during this process.
Treatment options
There are different treatment options depending on which stage you’re in. It is important to note that not all treatments are applicable for every patient. And your dentist/periodontist will recommend the most suitable treatment option for your individual needs. This includes the following:
- Non-surgical treatment – cleaning of the tooth root surfaces, sometimes with the use of local anaesthetic depending on severity/ sensitivity. If the disease has progressed too far, your dentist will recommend you seek assistance from a specialist to achieve the best results.
- Surgical treatment with a periodontist – in some cases, periodontal surgery is required to gain access to the root surface. The specialist will determine when non-surgical treatment is not achieving the results needed and more invasive treatment is required. Surgical treatment is performed when we need to: gain access to root surface, reduce depth of periodontal pockets, regenerate lost periodontal attachment, increase the amount of tooth showing above the gum and graft tissues into areas where gum tissue has been lost.
In some cases, antibiotics (oral or topical) may be required to assist with the treatment.
There are also various tooth replacement options available for lost teeth such as bridges, implants or and dentures.
How to prevent gum disease:
- Brush Twice Daily – Use fluoridated toothpaste and a soft-bristle toothbrush. Electric toothbrushes are also highly effective. Avoid using medium or hard-bristle manual toothbrushes, as well as excessive scrubbing, which can contribute to gum recession. If necessary, incorporate mouthwash into your routine. The recommended order of care is as follows: floss/ pikster to break the bacteria and plaque barrier, rinse with mouthwash, and then brush with toothpaste.
- Floss and/or Pikster Daily – Flossing helps remove plaque from between the teeth and below the gumline, areas that are difficult to reach with a toothbrush alone.
- Regular Dental Check-ups – Schedule visits at least twice a year for comprehensive examinations and professional cleanings. This ensures your gum health remains stable, and any issues are addressed early.
- Quit or Limit Smoking – Smoking is a significant risk factor for periodontal disease and oral cancer. Reducing or eliminating tobacco use can greatly improve oral health.
- Maintain a Balanced Diet – Consume a diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support optimal oral health. Drink plenty of water to keep the mouth hydrated, which also aids in the production and flow of saliva.
Periodontal disease is preventable with consistent oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups. Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing and potentially reversing the condition, preventing more severe complications such as tooth loss. If you experience any symptoms, seek professional dental care promptly to preserve your gum and overall oral health